
In the above picture, Mark is talking to Jane. The words inside the blue box are the exact words that he speaks.
Here is how we express this:

This is direct speech. Direct speech is when we report the exact words that somebody says.
In this English lesson, you will learn:
- The rules for writing direct speech.
- The correct punctuation.
- Vocabulary to report direct speech.
Reporting clause before the direct speech
The reporting clause of direct speech is the short clause that indicates who is talking. It is the clause that is outside of the inverted commas. It is therefore not the words being spoken.
We can write the reporting clause either before or after the direct speech. If the reporting clause is before the direct speech, we write it as follows:

Grammar rules – If the reporting clause is before the direct speech:
We write a comma (,) before the direct speech.
We write the exact words inside the inverted commas.
The first letter is a capital letter.
We write a full stop (.) before the closing inverted commas.
Reporting clause before a question or exclamation


If the reporting clause is before a question or exclamation:
We write a comma (,) before the direct speech.
We write the exact words inside the inverted commas.
The first letter is a capital letter.
We write a question mark (?) before the closing inverted commas.
or
We write an exclamation mark (!) before the closing inverted commas.
Reporting clause after the direct speech

If the reporting clause is after the direct speech:
We write the exact words inside the inverted commas.
The first letter is a capital letter.
We write a comma (,) before the closing inverted commas.
We write a full stop (.) at the end of the reporting clause.
Reporting clause after a question or exclamation


If the reporting clause is after a question or exclamation:
We write the exact words inside the inverted commas.
The first letter is a capital letter.
We write a question mark (?) before the closing inverted commas.
or
We write an exclamation mark (!) before the closing inverted commas.
We write a full stop (.) at the end of the reporting clause.
Advanced rules for direct speech
Sometimes we break up the direct speech into 2 parts:

The second part of the direct speech starts with a small letter if it is the same sentence as the first part of the direct speech.
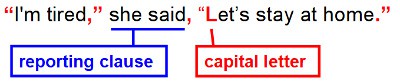
The second part of the direct speech starts with a capital letter if it is a new sentence.
Vocabulary of direct speech

We have several names for the above punctuation marks:
Inverted commas
Speech marks
Quotation marks
Quotes
Other reporting verbs
Here are some other useful reporting verbs:
reply (replied)
ask (asked)
shout (shouted)
agree (agreed)
comment (commented)
admit (admitted)
They are often used for writing direct speech in books, newspapers and reports. It is more common to use them in reporting clauses after the direct speech.
Examples:
“I really don’t like her dress,” she commented.
“I don’t love you anymore,” he admitted.
Other English lessons
Private online English lessons
How to pass the IELTS with a band 8
Adverbs of frequency
Indefinite article “a” and “an”
The prepositions FOR and SINCE
All of our lessons


Matěj Formánek says
How about this sentence:
I know the satnav is wrong!” exclaimed Zena. – Why the subject and predicate are swapped? It’s sentence from textbook so I’m confused.
Sagar says
Can we write multiple sentences in direct speech that comes before reporting clause?
In case if this is allowed, what punctuation mark should be used after the last sentence?
Example: “I entered the class room. As I did not find anybody there, I left the class room and went to buy a coffee.” explained the student to the teacher for his delay to come to the class.
Should the punctuation mark after the word coffee be comma instead of full stop?
Joaquim Barretto says
No full stop, but comma after the word coffee.
ola says
HI IM DAISY
courtney says
it is ok
Clare Hatcher says
Hello
I like the layout of this – very clear.
Just wondering if it is correct to use a comma in between two separate sentences in direct speech.
I think that now in published material you find this instead.
‘I’m tired,’ she said. ‘Let’s stay at home.’
Would appreciate your thoughts
Thanks
Layla says
If I wrote something with a comma at the end to continue speech like this:
“Hello,” he waved to the new student, “what’s you’re name?”
Do I have to use a capital letter even if I’m continuing with a comma or is it lowercase?
Sylvia Edouard says
Yes, you need to use a capital letter as speech from someone has to start with a capital letter. Always.
fuad says
which of the following is correct?
1. Should the status go missing when the metadata states, “Sign & return document?”
2. Should the status go missing when the metadata states, “Sign & return document,”? (comma inside)
3. Should the status go missing when the metadata states, “Sign & return document.”? (full stop inside)
Jan Švanda says
I presume the quotation is there to specify the exact phrase (for the metadata entry). I also encounter this from time to time, when writing technical documentation. I believe in that case you should write the phrase as it is, proper grammar be damned; beautifully looking documentation is useless if it leads to incorrect results.
In this case, I don’t even think this is “direct speech”, the metadata entry isn’t walking around and saying things, the quotation mark is there to indicate precise phrase – similar to marking strings in programming languages. Because of this, I don’t think direct speech rules apply, or at least, they should take back seat. If the expected status includes full stop at the end, the sentence would be:
4. Should the status go missing when the metadata states “Sign & return document.”? (no comma before, since it is not a direct speech; full stop inside, as it is part of the quoted status)
From grammatical perspective the end looks a bit ugly, but again, if this should be technical documentation, that is less important than precision.
A person says
One extra thing: YOU MUST NOT USE THE WORD SAID IN A REPORTING CLAUSE. EVER. IT’S UNIMAGINATIVE.
no joke, it’s actually discouraged and even close to banned at my school
Jan Švanda says
This is stupid. You shouldn’t use it in _every_ sentence, there should be variety, but outright banning it doesn’t make sense.
Case in point:
Book: ‘Pride and Prejudice’. Phrase to search: ‘,” said’ (comma, followed by quotation mark, followed by space, followed by word ‘said’). Number of occurrences: 211. Total number of ‘,”‘ (comma, followed by quotation mark) strings is 436, so “said” is used in almost 50% cases of direct speech of this type.
I don’t think it would be right for your school to ban Jane Austin, do you?
blaire says
How do you use names in direct speech?
Is it:
“I really don’t like her dress,” Ashley said.
or
“I really don’t like her dress,” said Ashley.
I’ve seen both and I’m so confused which one is correct, please help me.
Andrew says
Hello and thanks for your comment and question.
After the direct speech, both are correct.
Before the direct speech, only the first one is correct:
Ashley said, “I really don’t like her dress.” (correct)
Said Ashley, “I really don’t like her dress.” (wrong)
I hope that helps you.
Andrew
https://www.youtube.com/@CrownAcademyEnglish/